Symptoms and Treatments
Links:
Illustration of what happens to the neuron in an MS patient...
Before:
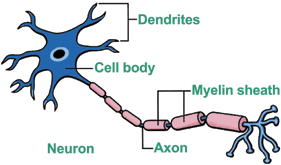
After:
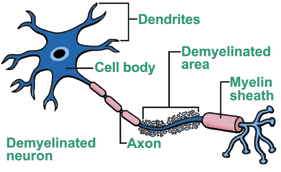
Symptoms
Symptoms are unpredictable varying from time-to-time and person-to-person. Symptoms are caused by the loss of myelin.
- Muscle weakness
- Spasticity
- Impairment of pain, temperature, touch senses
- Pain (moderate to severe)
- Ataxia
- Tremor
- Speech disturbance
- Vision disturbances
- Vertigo
- Bladder dysfunction
- Bowel dysfunction
- Sexual dysfunction
- Depression
- Euphoria
- Cognitive abnormalities
- Fatigue
Four General Types of MS:
Relapsing-Remitting:
Characteristics:
--defined flare-ups (relapses, attacks, or exacerbations)
--partial or complete recovery periods free of diease progression
Frequency:
--most common form of MS; approximately 85%
Primary-Progressive:
Characteristics:
--slow but continuous worsening of disease from onset
--no distinct relapses or remissions
--variations in rates of progression, occasional plateaus and temporary minor improvements
Frenquency:
--relatively rare; approximately 10%
Secondary Progressive:
Characteristics:
--initial period of relapsing-remitting disease followed by steadily worsening of disease
--with or without occasional flare-ups, remissions, or plateaus
Frequency:
--50% of people with relapsing-remitting MS develop this form within 10 years
Progressive-Relapsing
Characteristics:
--steadily worsening of disease
--acute relapses (attacks or exacerbations) with or without recovery
--periods between relapses characterized by continuing disease progression
Frequency:
--relatively rare; approximately 5%
Treatments
Treatments reduce the severity of the symptoms; however, they have no affect on the progression of MS
- Corticosteroids: reduce inflammation of CNS during relapse and increase recovery speed from relapse;however, there are many side effects.
- Immunosuppressants: ex: Mitoxantrone are used to suppress the actions of the immune system in patients with rapidly worsening MS.
- Interferon Beta: controls activity in the immune system and inhibits certain intracellular messages (i.e. cytockines). Cytokines, including interferon gamma, are considered to be involved in the inflammation process resulting in MS.
- Avonex
- Interferon Beta-1b
- Glatiramer Acetate (Copaxone)
Drugs Used to Treat Symptoms of Multiple Sclerosis:
Symptom |
Drug |
Spasticity |
Baclofen (Lioresal) Tizanidine (Zanaflex) Diazepam (Valium) Clonazepam (Klonopin) Dantrolene (Dantrium) |
Optic neuritis |
Methylprednisolone (Solu-Medrol) Oral steroids |
Fatigue |
Antidepressants Amantadine (Symmetrel) Pemoline (Cylert) |
Pain |
Aspirin or acetaminophen Antidepressants Codeine |
Trigeminal neuralgia |
Carbamazapine, other anticonvulsant |
Sexual dysfunction |
Papaverine injections(in men) |
from http://www.ninds.nih.gov/disorders/multiple_sclerosis/detail_multiple_sclerosis.htm#34173215
The best treatment for MS would be directed towards preventing irreversible damage to myelin and nerve fibers.
Statistics
- twice as women as men have MS
- it occurs more commonly among people of Northern European descent
- approximately 400,000 Americans have MS
- every week, 200 people are diagnosed with MS
- MS affects more than 2.5 million individuals
- most people are diagnosed with MS between the ages of 20 and 50; although, individuals as young as 2 and as old as 75 have developed the disease